Growing Bamboo In Washington
Bamboo cultivation in Washington is a feasible endeavor due to the region’s favorable climate and suitable growing conditions. With abundant rainfall and mild winters, this area provides an ideal environment for various bamboo species to thrive.
Climate and Conditions
The climate and conditions in Washington provide a favorable environment for growing bamboo, with abundant rainfall and mild winters that allow for a variety of bamboo species to flourish.
The Pacific Northwest region, including Northwest Washington, is mostly classified as USDA Hardiness Zone 8, which is suitable for bamboo cultivation. Some parts of Northwest Washington may drop to Zone 7 or even Zone 6 in certain areas. This diversity in hardiness zones opens up numerous choices for bamboo varieties that can thrive in the region.
When selecting bamboo for Washington’s climate, it is recommended to choose cold-hardy and clumping species to minimize invasiveness. Bamboo requires well-draining soil with organic content and ample sunlight for optimal growth. In areas with heavy clay soil, raised garden beds or containers can be used instead.
Planting bamboo rhizomes should be done in spring or summer to allow them time to establish before winter arrives. It is also important to provide adequate moisture during the initial stages until the plants sprout, after which natural rainfall should suffice. Proper spacing of rhizomes and mulching newly planted bamboo are essential practices for successful growth adaptation in this region.
USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Hardiness Zones are essential to determine the suitable climate for cultivating various plant species, including bamboo, in the Pacific Northwest.
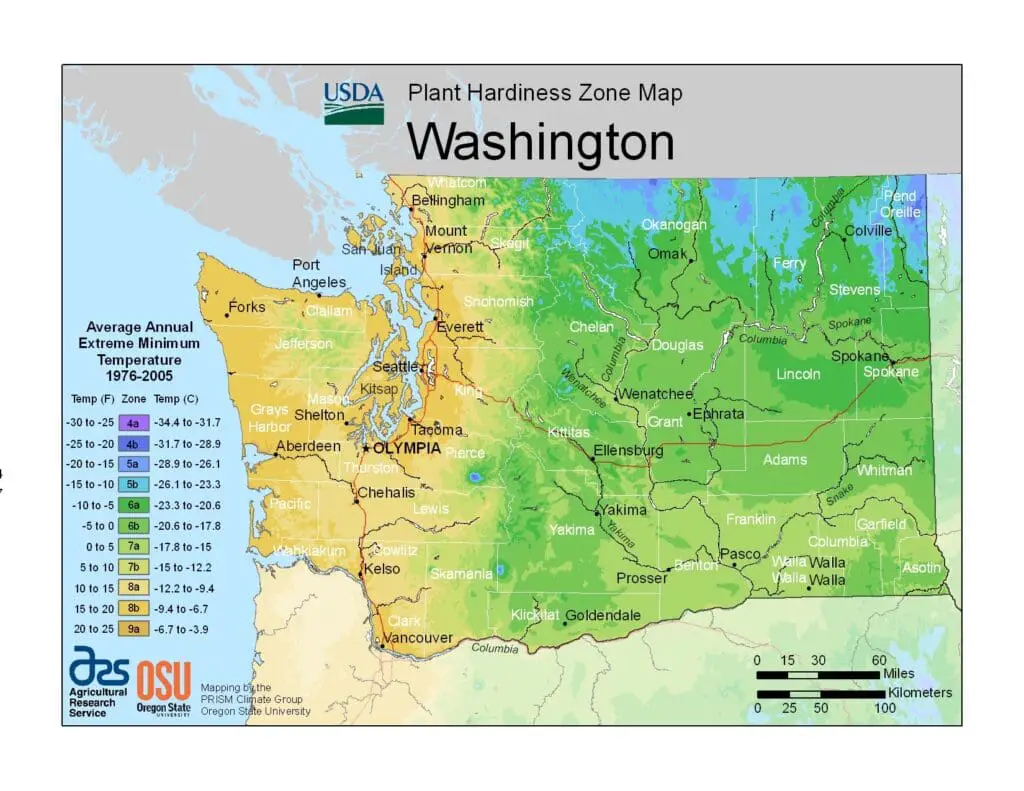
In Northwest Washington, which is mostly USDA Hardiness Zone 8 but can drop to Zone 7 or even Zone 6 in certain areas, there are ample options for growing bamboo.
For colder zones, it is recommended to choose bamboo varieties that can survive winter conditions.
When planting bamboo rhizomes, it is important to ensure proper spacing based on the specific species to avoid overcrowding or unwanted gaps.
Additionally, mulch plays a significant role in bamboo cultivation by providing insulation and preventing soil from drying out. Applying a layer of 1 inch of mulch around newly planted bamboo can help retain moisture and promote healthy growth.
Suitable Bamboo Species
Suitable bamboo species for cultivation in the Pacific Northwest include Bambusa oldhamii, Borinda fungosa, Chimonobambusa quadrangularis, Hibanobambusa tranquillans ‘Shiroshima’, Phyllostachys vivax, and Phyllostachys bambusoides. These bamboo species have been found to thrive in the mild climate of the Pacific Northwest region.
When selecting bamboo species, it is important to consider their growth habits. Clumping bamboos such as Bambusa oldhamii and Borinda fungosa tend to stay in tight clumps and do not spread aggressively. Running bamboos like Chimonobambusa quadrangularis and Phyllostachys vivax have a tendency to spread rapidly through underground rhizomes if not properly contained.
To prevent unwanted spreading, suitable containment measures should be implemented when growing running bamboo varieties. This can include digging trenches or using barriers such as root barriers or containers to restrict their growth.
By carefully selecting appropriate bamboo species and implementing adequate containment measures, successful cultivation of bamboo can be achieved in the Pacific Northwest region.
Planting and Soil
When considering cultivation of bamboo in the Pacific Northwest, it is important to understand the planting process and the role of soil in providing optimal conditions for growth. In order to create suitable growing conditions for bamboo, there are several options to consider.
1) Raised garden beds: These can be used if the soil in your area is heavy clay or poorly draining. By elevating the planting area, you can ensure proper drainage and prevent waterlogged roots.
2) Container gardening: If space is limited or you prefer to have more control over the spread of bamboo, planting it in containers is a viable option. This allows you to easily move or contain the plants as needed.
3) Soil preparation: Before planting bamboo, it is crucial to prepare the soil properly. Bamboo prefers well-draining soil with organic content. Adding compost or other organic matter can help improve fertility and drainage.
4) Mulching: Once planted, mulching around bamboo plants with wood chips or straw can help insulate them and prevent the soil from drying out too quickly.
By considering these options for raised garden beds, container gardening, and proper soil preparation, you can create an environment that promotes healthy growth and control over your bamboo plants in Washington’s climate.
Maintenance and Control
Maintenance and control of bamboo in the Pacific Northwest requires careful attention to pruning, containment, and regular monitoring to prevent its invasive spread and ensure its healthy growth.
Pruning techniques are essential for managing the size and shape of bamboo plants. This involves removing any dead or damaged culms, as well as thinning out dense clumps to promote air circulation.
Regularly checking for signs of pests or diseases is also crucial in maintaining the overall health of bamboo.
Containment methods such as barriers or trenches should be used for running bamboo species to prevent their aggressive spreading. These barriers should extend at least 2 feet below ground level to effectively contain rhizomes.
Additionally, regular monitoring is necessary to detect any signs of rhizome escape and promptly address them before they become a problem.
Benefits of Growing Bamboo
One advantage of cultivating bamboo in the Pacific Northwest is its ability to provide natural habitat and food sources for a diverse range of bird species. Bamboo, with its dense growth and tall culms, creates an ideal environment for birds to build nests and seek shelter. The presence of bamboo also attracts various insects, which serve as a valuable food source for birds.
Additionally, bamboo can contribute to the overall biodiversity of the area by providing nesting sites for other small animals like squirrels and rodents. Furthermore, bamboo cultivation offers several benefits that make it a sustainable and eco-friendly option for landscaping in Washington. Bamboo plants are known for their fast growth rate and ability to absorb large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thus helping reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, bamboo’s extensive root system helps prevent soil erosion and stabilize slopes. Overall, growing bamboo in Washington can not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also support local wildlife populations while contributing to environmental sustainability.
Specialized Support
To ensure the successful cultivation of bamboo in the Pacific Northwest, it is crucial to provide specialized support tailored to the specific needs and characteristics of this unique plant species. Bamboo support methods play a significant role in maintaining the structural integrity and promoting healthy growth of bamboo plants.
Bamboo structure design should consider factors such as height, weight, and spread of the bamboo culms to provide adequate support. Various techniques can be employed to facilitate proper bamboo growth, including staking or trellising young bamboo plants for stability, creating frameworks using sturdy materials like metal or wood for mature bamboo, and regularly pruning to maintain an optimal shape.
Consider Local Regulations
Consideration of local regulations is crucial when cultivating bamboo in the Pacific Northwest, as adherence to these guidelines ensures compliance with legal requirements and prevents potential conflicts or penalties.
It is important to familiarize oneself with the specific regulations regarding bamboo cultivation in Washington, as some regions may have restrictions due to concerns about invasive species and their environmental impact.
Local regulations may include rules on planting distance from property lines or neighboring properties to prevent encroachment, guidelines for the use of barriers or containment methods for running bamboo varieties, and permits for planting certain bamboo species.
Conclusion
In conclusion, growing bamboo in Washington is a feasible endeavor due to the region’s favorable climate and suitable species options. It is important to take measures to contain bamboo due to its invasive nature, using methods such as trenches or clumping bamboo.

